Program: C code to implement Linked List and Median Sort and Different Search Algorithms
Question 1

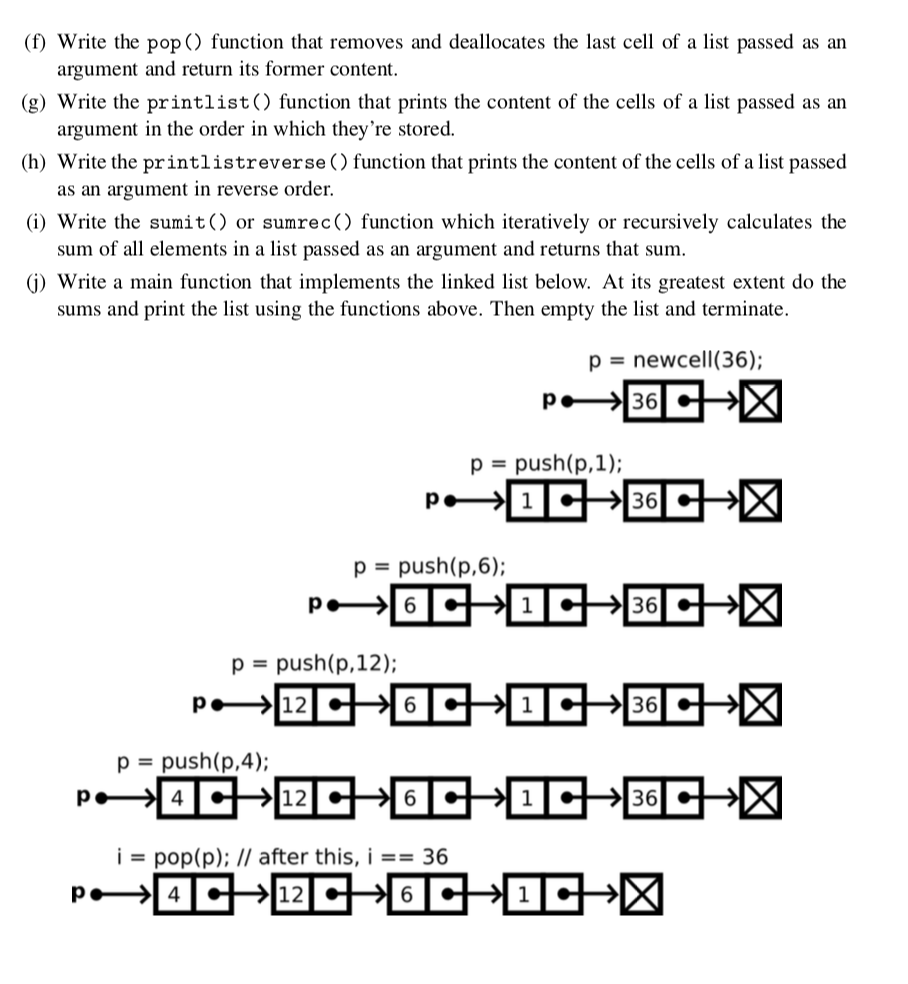
Solution
//gcc -o Question1 Question1.c
//./Question1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//Defining the struct.
struct cell{
int content;
struct cell *next;
};
//Assigning the struct variable a value to content and assigning null to next.
struct cell* newcell(int n)
{
struct cell *c = (struct cell*)malloc(sizeof(struct cell));
c->content = n;
c->next = NULL;
return c;
}
//Adding a new element to queue.
struct cell* push(struct cell *que, int num)
{
struct cell *q = newcell(num);
q->next = que;
return q;
}
//Function to count the number of cells in the queue
int countcells(struct cell *que)
{
struct cell *q = que;
int count = 1;
if(q->next != NULL)
{
while(q->next != NULL){
++count;
q = q->next;
}
printf("\n\nFinal number of elements %d\n\n", count);
}
else{
count = count;
}
return count;
}
// Function to dellocate memory after pop function
int deallocatelist(struct cell* q)
{
// Number of cells freed;
int cell_freed_count = 0;
free(q);
cell_freed_count++;
return cell_freed_count;
}
//Deleting the element in the queue.
int pop(struct cell *q){
int deleted_value = 0;
struct cell *next_node = q;
if (q != NULL)
{
/* code */
//If next->next pointer of queue is pointing to NULL then remove that element.
if(next_node->next != NULL){
while(next_node->next->next != NULL){
next_node = next_node->next;
}
deleted_value = next_node->next->content;
printf("Number of cells freed %d\n",deallocatelist(next_node->next));
next_node->next = NULL;
}
else{
deleted_value = next_node->content;
printf("Number of cells freed %d\n",deallocatelist(next_node));
next_node->next = NULL;
}
return deleted_value;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
// Function to print the list
void printlistreverse(struct cell* q){
struct cell *next_node = q;
if(next_node->next != NULL)
{
printf("\n\n\nReverse order of the list: \n");
while(next_node->next != NULL){
printf(" %d \t", next_node->content);
next_node = next_node->next;
}
printf(" %d \n", next_node->content);
}
else{
printf("\n\n\n\n Only one element in the list %d : \n", next_node->content);
}
}
//Function to print list in reverse order.
void printlist(struct cell* q){
if(q == NULL)
{
return;
}
printlist(q->next);
printf("%d \t", q->content);
}
//Function to calculate the sum of all the queue content values
int sumit(struct cell* q)
{
int sum = 0;
while(q->next != NULL)
{
sum = sum + q->content;
q = q->next;
}
sum = sum + q->content;
printf("\nSum of all the elements in the list is : %d \n", sum);
return sum;
}
//Main function.
int main()
{
struct cell *q;
q = newcell(36);
q = push(q,1);
q = push(q,6);
q = push(q,12);
q = push(q,4);
//printlist(q);
printf("\n\nElements in the list:\n");
printlist(q);
printlistreverse(q);
countcells(q);
sumit(q);
int delete_value = 0;
printf("******************************************\n");
printf("Deleting a value\n\n");
delete_value = pop(q);
printf("Deleted values is %d \n", delete_value);
countcells(q);
printf("Elements in the list:\n");
printlist(q);
printlistreverse(q);
sumit(q);
printf("******************************************\n");
//Empty the queue.
printf("\nDeleting values sequentially \n\n");
while(q->next != NULL)
{
delete_value = pop(q);
printf("Deleted cell value is: %d \n\n", delete_value);
}
delete_value = pop(q);
printf("Deleted last value and emptyed the list: %d \n\n", delete_value);
//Number of elements in the queue.
int count = countcells(q);
//Since we had initialzed count to 1 in countcell function so we are subtracting the count value here, so that we get the exact number of elements in queue.
printf("Number of elements after removing all the elements in the queue = %d\n\n",count-1);
return 0;
}
Question 2



Solution
//gcc -o Question2 Question2.c //./Question2
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<ctype.h>
//Function to generate n random number between 0 and max
int * randomArray(int n, int max)
{
int c;
int *arr = (int *)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
arr[c] = rand() % (max+1) ;
}
return arr;
}
//Function to median of an array passed
int median(int n, int *arr)
{
if(n<=0)
{
return -1;
}
int i,j;
//Initializing median to -1;
int final_median = -1;
//min_diff:difference between number of elements greater than selected element in array and number of elements lesser than selected element
//max_diff:sum of number of elements greater than selected element in array and number of elements lesser than selected element
//position is the element position in the unsorted array.
int min_diff, max_diff, position;
int counter_3 =0;
//Loop for each element in the array
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
//Counters
int counter = 0;
int counter_1 =0;
//Greater stores number of elements greater than selected ith element
int greater = 0;
//Lesser stores number of elements lesser than selected ith element
int lesser = 0;
//Rep to store number of replicates of selected element in the array
int rep = 0;
//diff to store the diff between greater than lesser counters.
int diff = 0;
for(j = 0; j<n; j++){
//leaving out the ith element
if(j!=i){
//Calculating number of greater element for the ith number.
if(arr[i]<arr[j])
{
greater++;
}
//Calculating number of lesser element for the ith number.
else if(arr[i] > arr[j])
{
lesser++;
}
}
//Calculating the number of elements equal to ith value.
if(arr[i] == arr[j])
{
rep++;
}
}
//calculating the difference between greater and lesser counters
diff = abs(greater - lesser);
//if number of elememts in array are odd
if(n%2 != 0){
//Checking if diif == 0, becasue if diff == 0 then setting that ith element as median.
if(diff == 0){
position = i;
final_median = arr[i];
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
else if((diff+1)== rep)
{ position =i;
final_median = arr[i];
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
else if(diff < rep)
{
position = i;
final_median = arr[i];
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
else if (rep%diff != 0)
{
if((diff) < rep)
{
position = i;
final_median = arr[i];
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
}
}
//If number of elements in array are even
else{
if(i == 0)
{
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
}
else{
if((abs(diff - rep) <= min_diff) && (rep > 1) && (arr[i]<final_median)&& (abs(diff + rep) < max_diff)){
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
}
else if((abs(diff - rep) <= min_diff) && (rep > 1) && (arr[i]>final_median) && (abs(diff + rep) < max_diff))
{
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
}
else if((abs(diff - rep) == 0) && (rep > 1) && (arr[i]<final_median) )
{
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
}
else if(rep == 1 && ((abs(diff - rep) == 0 ))&& arr[i] < final_median)
{
if(counter == 0)
{
position = i;
final_median = arr[i];
counter++;
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
else{
if(arr[i] < final_median)
{
position = i;
final_median = arr[i];
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
}
}
else if(rep == 1 && (abs(diff - rep) < min_diff))
{
if(counter_1 == 0)
{
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
counter_1++;
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
else{
if(arr[i] < final_median)
{
final_median = arr[i];
position = i;
min_diff = abs(diff - rep);
max_diff = abs(diff + rep);
}
}
}
}
}
}
//loop which removes the median element from the array and moves all the elements after if to left by 1, this loop is helpful for recursive mediansort
for(i = position; i<n-1;i++)
{
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
}
//Setting last element in the array to 1
arr[n-1]= -1;
//returning the median value found to calling function.
return final_median;
}
//counters to store position of median and number of elements in the array passed.
int position;
int number_values;
//Median sort function
void medianSort(int n, int *cycle, int *arr,int *sorted){
int i;
//If number of elements passed is greater than 0
if(n>0){
//calling median function to return median of the array passed
int mid_value = median(n,arr);
//for first cycle
if(*cycle == 0)
{
number_values = n;
//if array size is even.
if(n%2 == 0)
{
position = n/2 - 1;
sorted[position] = mid_value;
}
// if array size is odd
else{
position = n/2;
sorted[position] = mid_value;
}
}
//Cycles > 0
else
{
int i = position;
//if array size is even
if((n%2 == 0))
{
if(mid_value > sorted[position])
{
goto loop1;
}
loop : while(sorted[i-1] != -1 && (i)>= 0)
{
if(sorted[i-1] < mid_value)
{
int temp = sorted[i-1];
sorted[i-1] = mid_value;
mid_value = temp;
}
i--;
}
sorted[i-1] = mid_value;
}
else{
if(mid_value < sorted[position])
{
goto loop;
}
loop1: while(sorted[i+1] != -1 && (i+1)<= number_values)
{
if(sorted[i+1] > mid_value)
{
int temp = sorted[i+1];
sorted[i+1] = mid_value;
mid_value = temp;
}
i++;
}
sorted[i+1] = mid_value;
}
}
//incrementing the cycle
++*cycle;
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------cycle:%d\n", *cycle);
int i;
printf("\n");
for(i = 0; i<(n+*cycle-1); i++)
{
printf("%d\t", sorted[i]);
}
printf("\n");
//printf("-------------------------------------------------------------------------end \n\n");
medianSort(n-1, cycle, arr, sorted);
//printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------end\n\n");
}
}
// Naive serach
int search(int i, int n, int *arr)
{
int c;
for(c = 0; c<n; c++)
{
//Checking if ith array element is equal to search element return position
if(arr[c] == i)
{
return c;
}
//If ith array element found is greater than search element return -1
else if(arr[c] > i)
{
return -1;
}
}
//If nothing is found sorted array return -1
return -1;
}
//ChopSearch Function.
int chopsearch(int i, int n, int *arr, int amin, int amax)
{
//If amax == amin and serach element is not equal to array of amax return -1 because we have nothing to proceed further.
if((amax==amin) && (i != arr[amax]))
{
return -1;
}
//If amax == amin and amax element is equal to search element then we no need to proceed left or right as this will be the samllest index of serach element.
if((amax==amin) && (i == arr[amax]))
{
return amax;
}
//If amax > amin the we generate random number and move accordingly.
if(amax>=amin){
//Generating the random number.
int x =(rand() % (amax - amin + 1)) + amin;
//If search element is equal to xth element in array the move left to find the minimum index;
if(i == arr[x]){
//Moving left until serach element not equal to xth element of array
while(arr[x] == i){
--x;
}
return (x+1);
}
//If search element is less than xth element in the array then move left and search again.
if(i < arr[x]){
amax = x-1;
if(amax < 0)
{
return -1;
}
else{
return (chopsearch(i, n,arr, amin, x-1));
}
}
//If search element is greater than xth element in the array then move right and search again.
if(i > arr[x])
{
amin = x+1;
if(amin >=n)
{
return -1;
}
else{
return chopsearch(i, n,arr, amin, amax);
}
}
return -1;
}
//If amax < amin the we return -1.
else
{
return -1;
}
}
// Benchmark naive function
double benchmark_naive(int n, int max, int s, int mult)
{
printf("Entered the naive\n");
time_t start,end;
//Starting the timer.
start=clock();
int i,counter =0,j;
int return_value;
int * array_1;
int * sorted_1;
for(i = 0;i<mult; i++)
{
//Generating random array and sorting for every 1000th iteration
if(i%1000 == 0){
counter++;
array_1 = randomArray(n,max);
sorted_1 = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for(max = 0; max<n; max++){
sorted_1[max] = -1;
}
int cycle_init = 0;
int *cycle_1 = &cycle_init;
medianSort(n, cycle_1, array_1, sorted_1);
printf("naive value = %d\t, counter=%d\n",s,counter);
}
//Searching the element in the sorted for mult times using normal search
return_value = search(s, n, sorted_1);
}
float t;
//Ending the clock after n iterations
end=clock();
t=(end-start);
//Freeing the memory allocated to arrays
free(array_1);
free(sorted_1);
printf("time = %f\n", t);
return t;
}
//Benchmark Chop
double benchmark_chop(int n, int max, int s, int mult)
{
printf("Entered the chopsearch\n");
//Starting the timer
time_t start,end;
start=clock();
int i,counter =0,j;
int return_value;
int * array_1;// = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
int * sorted_1;// = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for(i = 0;i<mult; i++)
{
//Genrating the random array and sorting for every 1000th iteration
if(i%1000 == 0){
counter++;
array_1 = randomArray(n,max);
sorted_1 = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
for(max = 0; max<n; max++){
sorted_1[max] = -1;
}
int cycle_init = 0;
int *cycle_1 = &cycle_init;
medianSort(n, cycle_1, array_1, sorted_1);
printf(" chopsearch value = %d\t, counter=%d\n",s,counter);
}
//Searching the element in the sorted array for mult times using chop serach
return_value = chopsearch(s,n,sorted_1,0,n-1);
}
float t;
//Stoping the clock
end=clock();
t=(end-start);
//Freeing the memory allocated to array's
free(array_1);
free(sorted_1);
printf("time = %f\n", t);
return t;
}
int main(){
int max, n, median_value = 0;
int * array;
printf("\nEnter random array size\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
if(n<=0)
{
printf("Wrong input, please enter size of arary greater than or equal to 1\n");
return -1;
}
printf("\nEnter the maximum value of random number\n");
scanf("%d", &max);
if(max<0)
{
printf("Wrong input, please enter max value greater than or equal to 1\n");
return -1;
}
//Generating the random array between 0 and max
array = randomArray(n,max);
int cycle_init = 0;
int *cycle_1 = &cycle_init;
int *sorted = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
//Printing the random array
printf("\nRandom Array genrated \n");
for(max = 0; max<n; max++){
printf("%d\t", array[max]);
sorted[max] = -1;
}
printf("\n\nFinding Median and sorting the array \n");
printf("\n---------------------------------------------------------------------cycle:%d\n", *cycle_1);
for(max = 0; max<n; max++){
printf("%d\t", sorted[max]);
}
printf("\n");
int i;
medianSort(n, cycle_1, array, sorted);
printf("\n\n\n");
printf("Sorted Array is:\n");
//Printing the sorted array
for(max = 0; max<n; max++){
printf("%d\t", sorted[max]);
}
printf("\n-------------------------------------------------------------------------end \n\n");
printf("\n\n");
int g;
printf("-------------------Enter the number you want to search----------------------- \n");
scanf("%d", &g);
//Serarching the number entered both using normal serach and chop serach and printing the minimum index if found else -1(if search element in not found)
int min_index = search(g, n, sorted);
printf("Normal Search Index =%d\n",min_index);
int min_index_chopsearch = chopsearch(g,n,sorted,0,n-1);
printf("Chop Search Index =%d\n",min_index_chopsearch);
printf("\n\n---------------End -------------\n");
//Below commented code for calling bench mark code for both naive and chop benchmark.
/*
double time_n_10 = benchmark_naive(2000, 10000, 10, 1000000);
printf("Completed Naive search for 10\n\n");
double time_n_5000 = benchmark_naive(2000, 10000, 5000, 1000000);
printf("Completed Naive search for 5000\n\n");
double time_n_9000 = benchmark_naive(2000, 10000, 9000, 1000000);
printf("Completed Naive search for 9000\n\n");
double time_c_10 = benchmark_chop(2000, 10000, 10, 1000000);
printf("Completed Chop search for 10\n\n");
double time_c_5000 = benchmark_chop(2000, 10000, 5000, 1000000);
printf("Completed Chop search for 10\n\n");
double time_c_9000 = benchmark_chop(2000, 10000, 9000, 1000000);
printf("Completed Chop search for 10\n\n");
printf("Naive Search Time\n");
printf("Searching 10 in Naive search = %f\n", time_n_10);
printf("Searching 10 in Naive search = %f\n", time_n_5000);
printf("Searching 10 in Naive search = %f\n", time_n_9000);
printf("Chop Search Time\n");
printf(" Searching 10 in chopsearch = %f\n", time_c_10);
printf(" Searching 5000 in chopsearch = %f\n", time_c_5000);
printf("Searching 9000 in chopsearch = %f\n", time_c_9000);
*/
printf("\nFollowing are the output obtained for benchmark naive \n");
printf("For Searching 10, time taken is 16422836224 clocks per second\n");
printf("For Searching 5000, time taken is 16675453952 clocks per second\n");
printf("For Searching 9000, time taken is 16960251904 clocks per second\n");
printf("Time taken to execute is expected to increase as search element index increases, which we can see in the above output. \n\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("\nFollowing are the output obtained for benchmark chop \n");
printf("For Searching 10, time taken is 16580889600 clocks per second\n");
printf("For Searching 5000, time taken is 16567494656 clocks per second\n");
printf("For Searching 9000, time taken is time = 16824466432 clocks per second\n");
printf("Time taken to execute is expected to increase/decrease based on the randon index generated in chopsearch function, which we can see in the above output. \n\n");
printf("-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Time Complexity of Naive Search: \n Best Case : Big-O(1) \n Average Case : O(n) \n Worst Case : Big-Omega(n) \n\n");
printf("Time Complexity of Chop Search: \n Best Case : Big-O(1) \n Average Case : O(log(n)) \n Worst Case : Big-Omega(log(n)) \n\n");
printf("Time Complexity of Sorting : \n Best Case : Big-O(n^3) \n Average Case : O(n^3) \n Worst Case : Big-Omega(n^3) \n\n");
}

