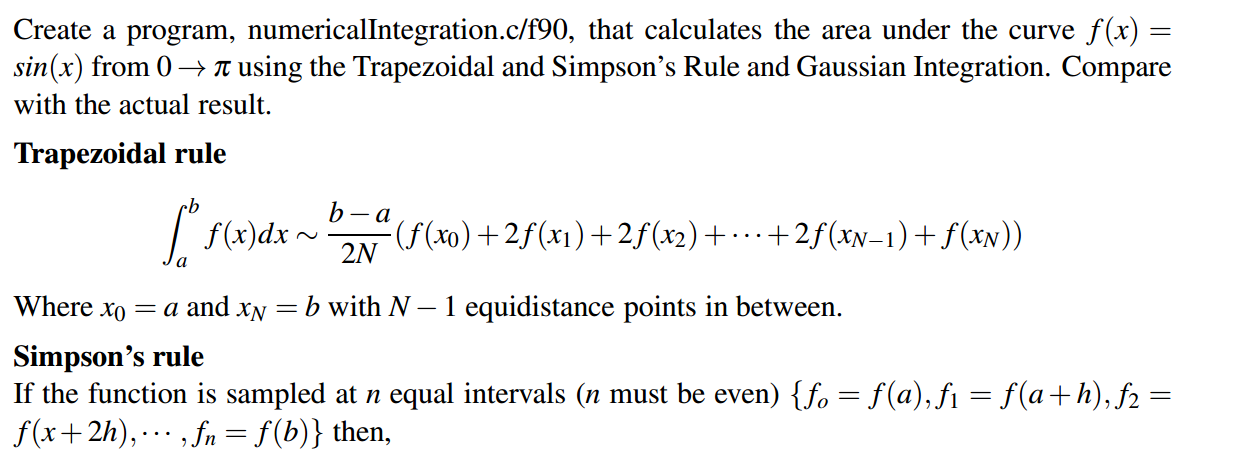
Program: C code to find Determinant of 3*3 matrix and Area of Curve(Trapezoidal Rule)
Here is the code to calculate 3*3 matrix determinant(Normal Matrix, Hilbert Martix) and by using Cramers rule to calculate determinant of matrix.
Commands to execute programs:
- Please remove “.txt” extension from Makefile.
- Running Commands:
- Question 1 : gcc -o question1 question1.c -lm ./question1
- Question2: Just type make in the command line as show below. make “To Clean run” : make clean
Question 1

Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Creating a structure to access 3x3 matrix
struct pmclass{
float exam[3][3];
};
// Calculating the determinant of each of the 3x3 matrix
float det(struct pmclass mat[],int ln){
float det = 0;
det = mat[ln].exam[0][0]*((mat[ln].exam[1][1]*mat[ln].exam[2][2]) (mat[ln].exam[2][1]*mat[ln].exam[1][2])) -mat[ln].exam[0][1]*(mat[ln].exam[1][0]*mat[ln].exam[2][2] - mat[ln].exam[2][0]*mat[ln].exam[1][2]) + mat[ln].exam[0][2]*(mat[ln].exam[1][0]*mat[ln].exam[2][1] - mat[ln].exam[2][0]*mat[ln].exam[1][1]);
//printf("Determinant %e \n", det);
return(det);
}
int main(){
int row, col, i;
//Hilbert Matrix
float mat[4][4];
printf("Hilbert Matrix is : \n\n");
//Calculating the hilbert matrix values
for (row = 0; row<4;row++)
{
for(col = 0; col<4; col++)
{
mat[row][col] = (float) 1.0/((row+1)+(col+1)-1.0);
printf(" %f", mat[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
float mat[4][4] = {
{1,0.5,0.33,0.25},
{0.5,0.33,0.25,0.2},
{0.33,0.25,0.2,0.16},
{0.25,0.2,0.16,0.14}
};
//Creating the structure pointer variables
struct pmclass *pmc;
// Allocating the memory, here we are mulitplying by 4 because we are going to get four 3x3 matrices.
pmc = (struct pmclass*) malloc(4 * sizeof(struct pmclass));
// sign variable to store the sign as we need alternating signs to calculate the determinant.
int sign = 1;
float ans = 0;
for(i = 0; i<4;i++) //For each of the struct we are creating 3x3 matrix.
{
int k =0, j=0;
for(row = 0; row<4; row++) //row and col to obtain the particular values from hilbert matrix.
{
for(col = 0; col<4; col++)
{
if(row != 0 && col != i) //Here we are ignoring the first row and particular column to for each 3x3 matrix.
{
// Storing the hilbert matrix values into our struct matrix. Here pmc[i] represents different 3x3 matrix
pmc[i].exam[j][k] = mat[row][col];
// Incrementing the column value of the struct 3x3 matrix.
k = k + 1;
// Checking if 3rd column is value is stored in struct 3x3 matrix
if(k == 3)
{
// Once the 3rd column value is extracted we are moving to next row and making the column to zero.
k = 0;
j = j + 1;
}
}
}
}
// mat[0][i] for obtaining the particular values of first row of hilbert matrix and det() call the determinant to calculate determinant of 3x3 matrix.
ans += sign * mat[0][i] * det(pmc, i);
// While calculating the determinant as we need alternating signs, so we changing the sign to -sign.
sign = -sign;
}
// Freeing the memory allocated to the pointer struct.
free(pmc);
// Printing the determinant of Hilbert 4x4 matrix.
printf("Determinant of above Hilbert matrix = %e \n\n", ans);
}
Question 2:
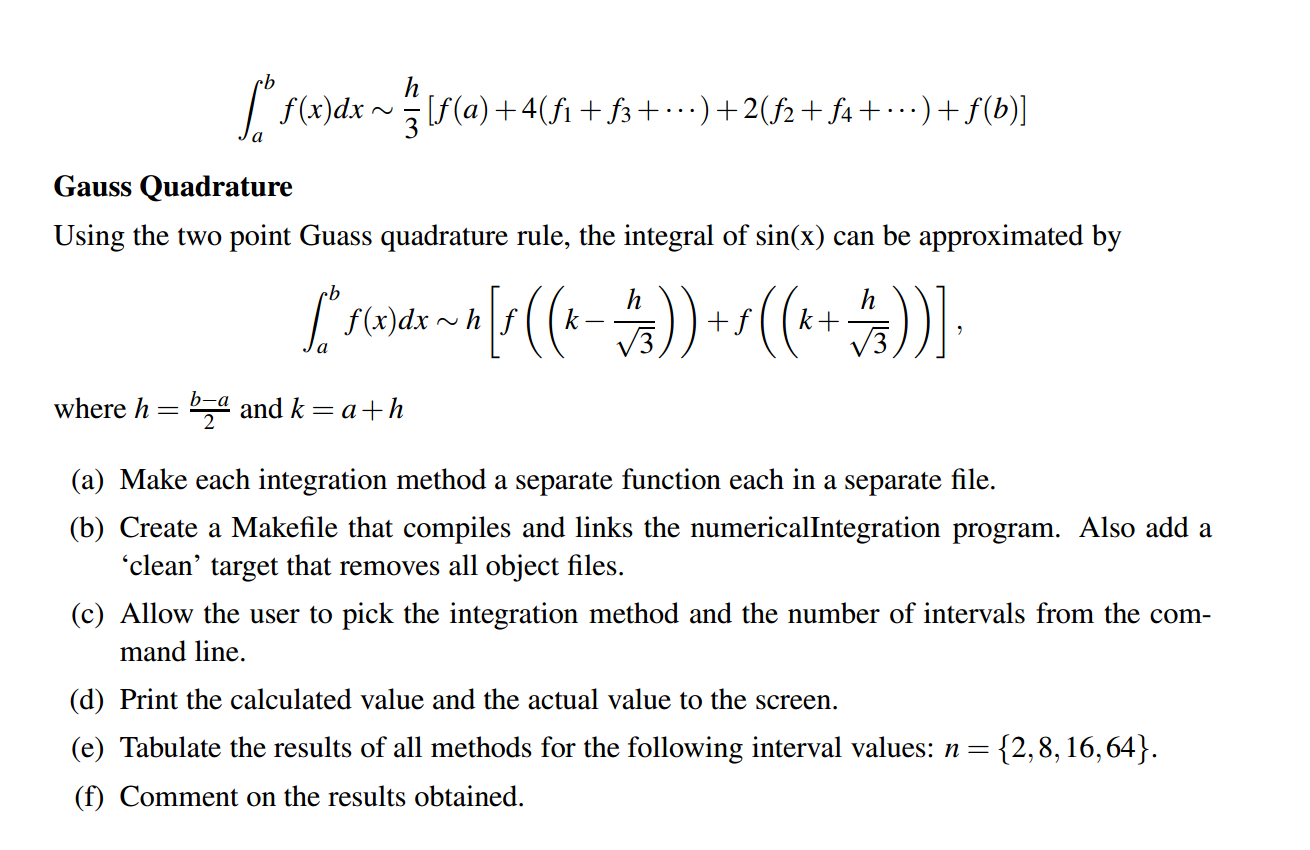
functions.h
// Trapezoidal function
float Trap(int);
// Simpson function
float Simpson(int);
// Gauss Rule.
float Gauss(void);
numericalIntegration.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "functions.h"
int main(){
// Obtaining the user input for particular functions value.
int num;
// Obtaining the user input for integral for which we need to calculate the value from the above functions given by user
int nint;
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Please enter number \n 1-Trapezoidal Rule: \n 2-Simpson's Rule: \n 3-Guass Quadrature \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("\n -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
// If user want Gauss value then user need not enter the integral value as it will be same for all of the integral values.
if(num != 3)
{
printf("\n\n***************************************************************************************\n");
printf("Enter the number of intervals \n");
scanf("%d,\n", &nint);
printf("\n****************************************************************************************\n");
}
printf("\n\n----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
// Storing the values obtanied from the function.
float x = 0;
// Checking what user has entered and executing the particular function.
if(num == 1)
{
x = Trap(nint);
printf("Calculated value = %f \n", x);
}
else if(num == 2)
{
x = Simpson(nint);
printf("Claculated value = %f \n", x);
}
else if(num == 3){
printf("No need of number of Integrals \n");
x = Gauss();
printf("Calculated value = %f \n", x);
}
else{
printf("You have entered wrong number \n");
}
printf("Actual Value = 2");
printf("\n----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
// Tabulating the values obtained from all the functions for the n values 2,8,16,64.
printf("\n\n\n\nTabulated Result of three methods for n={2,8,16,64}: \n\n\n");
printf("n,\t\t2\t\t8\t\t16\t\t64 \n");
printf("Trapezoidal \t%f\t%f\t%f\t%f\n", Trap(2),Trap(8),Trap(16),Trap(64));
printf("Simpson \t%f\t%f\t%f\t%f\n", Simpson(2),Simpson(8),Simpson(16),Simpson(64));
printf("Gauss \t\t%f\t%f\t%f\t%f", Gauss(),Gauss(),Gauss(),Gauss());
printf("\n\n Comments on Output \n");
printf(" 1. As 'n' value increases the output values tends to be accurate i.e; as n value increases the output values tends to reach 2.\n 2. There is no need of n values for Gauss Rule as it doesn't depend on the n.\n 3. Only in Simpson method for inital n values the output is above 2 and then as n increases the output tends to 2.\n 3. Only Simpson method gives us the exact output value for any values of n>= 64\n 4. Gauss Rule and Trapezoidal methonds provides output values less than 2 and later as n increases output tends to 2. \n ");
printf("\n\n\n............... Exiting............ \n\n\n");
return 0;
}
Simpson.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include "functions.h"
float Simpson(int N){
// Initital integral value
float a=0;
// Final integral value
float b = M_PI;
float h,ans;;
int i;
// Storing the function of initial integral and final integral.
float initial = 0.0;
initial = sin(a)+sin(b);
// Calculating the equal intervals
h = (b-a)/N;
//Storing the values, oddSum to store the values of odd functions and evenSum to store the values of even functions.
float oddSum = 0.0, evenSum = 0.0;
for(i=1;i<N;i++)
{
// Identifing if i is even or odd
if(i%2 == 0)
{
// if i is even then store the function value in evenSum.
evenSum = evenSum + sin(i*h);
}
else{
//if i is odd then storing the function value in oddSum
oddSum = oddSum + sin(i*h);
}
}
// Calculating the values.
ans = (h/3)*(initial+(4*oddSum)+(2*evenSum));
return ans;
}
Trapezoidal.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "functions.h"
#include<math.h>
float Trap(int N){
//Storing the initla integral value
float a=0;
//Storing the final integral value
float b = M_PI;
float h,y,ans;
// For storing the final value
float sum = 0;
int i;
// Storing the sum of values of function of initial and final integral.
float initial = 0;
initial = sin(a)+sin(b);
// Obtaining the equidistance.
h = (b-a)/(N);
//Calculating the value of all the numbers between inital and final integral.
for(i=1;i<(N);i++)
{
sum = sum + 2*sin(i*h);
//printf("%f \n", sum);
}
// Final value.
ans = (h/2)*(initial+sum);
//printf("Trapezoidal Valuev %f \n",ans);
return ans;
}
Gauss.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include "functions.h"
#include<math.h>
// Function to calculate the value using Gauss Rule.
float Gauss(void)
{
// Storing the initial of the integral
float a=0;
// Storing the final value of the integral
float b = M_PI;
float h,k,ans;
// calculating the equal intervals
h = (b-a)/2;
k = a+h;
//Calculating the value.
ans = (h)*(sin(k - (h/sqrt(3))) + sin(k+(h/sqrt(3))));;
return ans;
}
Makefile.txt
#Dependencies : Executing all the commands in hello.out
#Target : Running the ./a.out (output) file
all: hello.out
./a.out
#Dependence : To create the .o files of the function files
#Target : Executing the .o file to create output file.
hello.out: numericalIntegration.o Trapezoidal.o Simpson.o Gauss.o
gcc numericalIntegration.o Trapezoidal.o Simpson.o Gauss.o -lm
#Target : Executing the .c files to create .o files of main file.
numericalIntegration.o: numericalIntegration.c functions.h
gcc -c -Wall numericalIntegration.c -lm
Trapezodial.o: Trapezoidal.c functions.h
gcc -c -Wall Trapezoidal.c -lm
Simpson.o: Simpson.c functions.h
gcc -c -Wall Simpson.c -lm
Gauss.o: Gauss.c functions.h
gcc -c -Wall Gauss.c -lm
#Cleaning the object and output file from the memory.
clean:
rm *.o *.out

